The XXI century is forcing a focus on energy efficiency and ecology to reduce raw material, energy and fuel consumption. The thermal properties of wood as a material are limited, but log buildings must also be able to adapt to EU directives, regulations and requirements for new buildings. Log walls must also meet heat standards. How to ensure this, what to do?
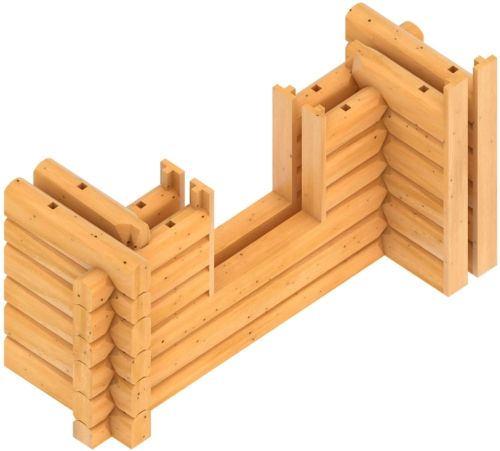
The idea is quite simple – to create double external walls around the log building. Or in part, just for one of the premises. The technical solution of the idea is much more complicated, because only equipment with high processing accuracy can create double walls. Accuracy is a must, as the external walls must be joined with dovetail joints and a huge number of corner joints must be made. Miniature and compact bonds of building corners consisting of four corner joints. In terms of quality, cost and productivity, it is hopeless to make them by hand, because even drawing of joints is very difficult.
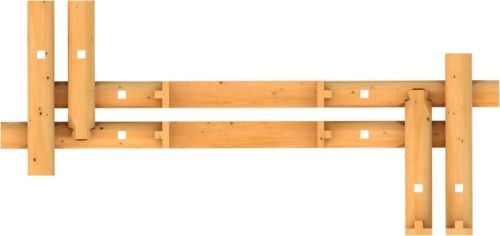
What does such a double-walled solution give?
- You will get a house with excellent heat resistance, i.e. the so-called U-value, but not only. In the case of a log building, also a breathable, ecologically clean and healthy house. The distance between the walls can be increased as needed, if you want to achieve a passive house UV standard of 0.1–0.15 W/(m²K). Only ecological, wood fibre insulation wool shall be used between the walls. Laboratory tests have not been performed yet, but it is predicted that the U value will not exceed 0.25 W/(m²K) at a gap of 100 mm between the log walls. The tests will soon be performed at one of the ENBRI (European Network of Building Research Institutes) Scandinavian institutions.
- The traditional look of the building, the same log ends and bonds of building corners remain both inside and outside. It will be very difficult to determine that the building has double external walls, because they are not visible anywhere – neither inside nor outside. The fact is conveyed only by the deeper openings of the outer walls, but rarely anyone pays attention to that. In addition, windows and doors in the openings can be positioned both in the middle and more inwards or outwards. The exception is intensively glazed walls, there is no sense in creating double walls there.
- The essence of the log building, the whole sense of this construction is preserved. The walls of the log building will not have to be forcibly covered with non-breathable additional frames and boards. It will not be necessary to cover the logs for which such a house is built at all. There will be no need to circumvent building codes, delay cladding or commissioning the building. You will not have to convince of the true thermal properties of the logs, fight with construction inspectors, insurers, etc.
- Both the settling of double walls and the removal of moisture from their intermediate space have been solved. The roof structure of a log house initially rests on the inner perimeter and inner walls, while when the building is settling, the roof is starting to rest on the outer perimeter walls. The air humidity is regulated and the theoretically possible small intermediate space condensate is absorbed and returned by the top layer of logs. Moisture exchange is also facilitated by wood fiber insulation material. The intermediate space is connected to the roof ventilation lathing via the insect screen in both directions.
- In the case of double walls, the logs have a homogeneous moisture content of the wood, however different in its localization. Almost all indoor walls and structures are in similar – homogeneous and very dry conditions, because the protection of the building against moisture and climatic effects is realized by the outer perimeter of the double walls. Only these logs have to deal with changing weather conditions! At least in this case, they are not disturbed by the difference between indoor and outdoor humidity and/or temperature.
- As stated in the introduction, it is possible to insulate part of the building or only some of the premises, and thus ensure the minimum heat resistance indicators of the building specified by law and required by the Construction Board. However, if you create double walls around the building (with the exception of intensively glazed facades), then in the long run you will save significantly more money, and the investment will pay off faster. Because, you will save more and regularly on heating costs.
What is the economic side of this?
As you know, the production of a log building frame is a small part of the total construction budget. But it is the part that is the most difficult, demanding and the most important part in every way. The part of why this was launched at all. The part around which everything is carefully designed, created and arranged. Unambiguously, the central part. It involves not only hopes and dreams, but also absolutely all financial investments.
Of course, there is a big difference whether you buy a new or used log building, how expensive and respectable the land plot is, whether the construction is organized by you or an elite contractor, how high quality, how finely decorated, how equipped it is, etc. It is clear that you have to be very careful with the low price, because it is more often characterized by not very high quality. So, there is a huge risk of ruining everything. In addition, different attitudes to quality are possible, even diametrically opposed. For example, in post-Soviet countries, log buildings still have the reputation of being the cheapest building.
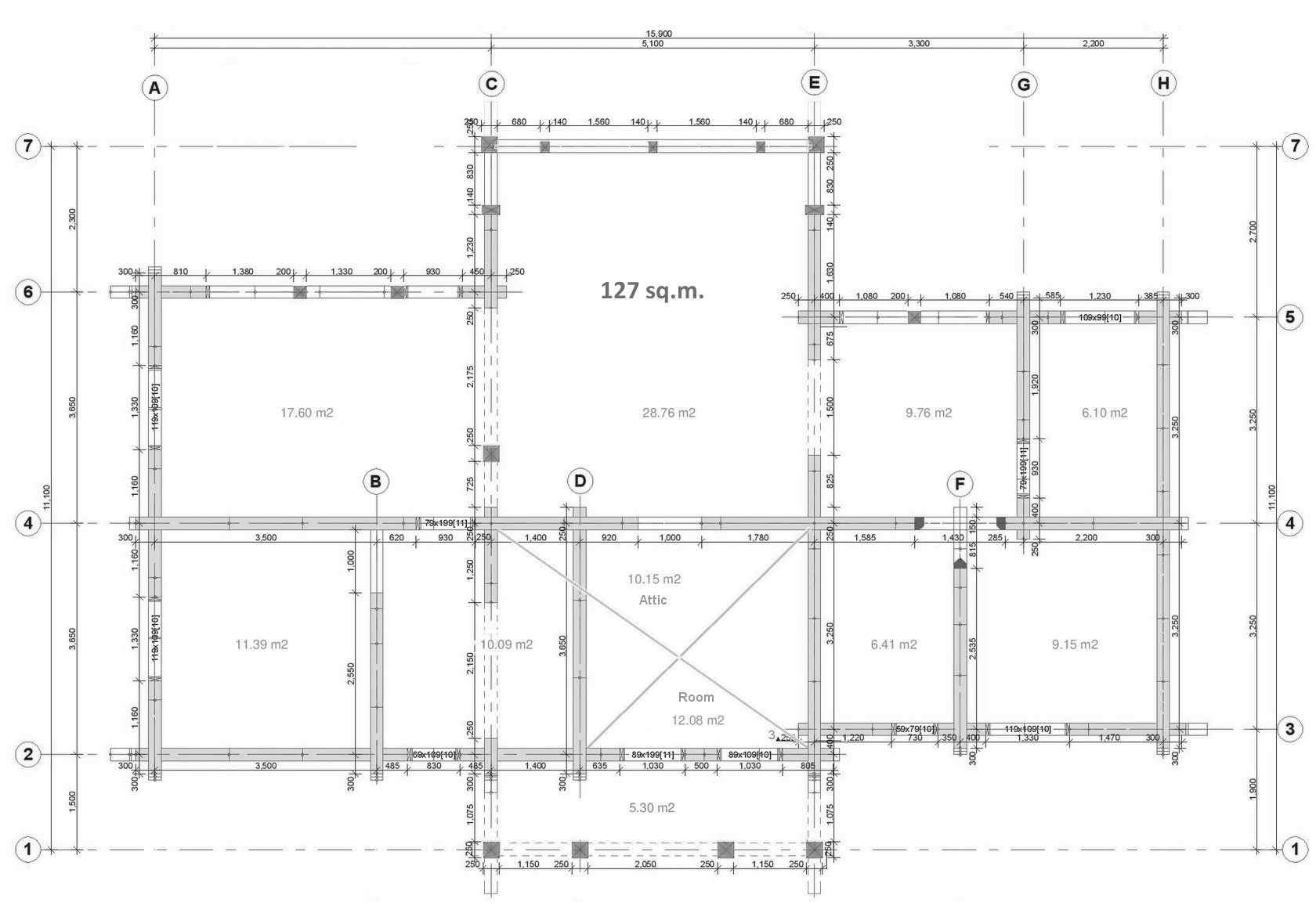
Okay, and what is the increase in the price of the frame for different double-walled versions or insulation levels? For partial insulation of external walls it is about 10 to 20% and if double external walls are formed around the house, then 30–50%. Here is a clear example of the costs of manufacturing a single-storey log building (127m²) frame, excluding VAT and delivery. For your information, the smaller the log building is and if it is a one-story building, the higher the costs are.
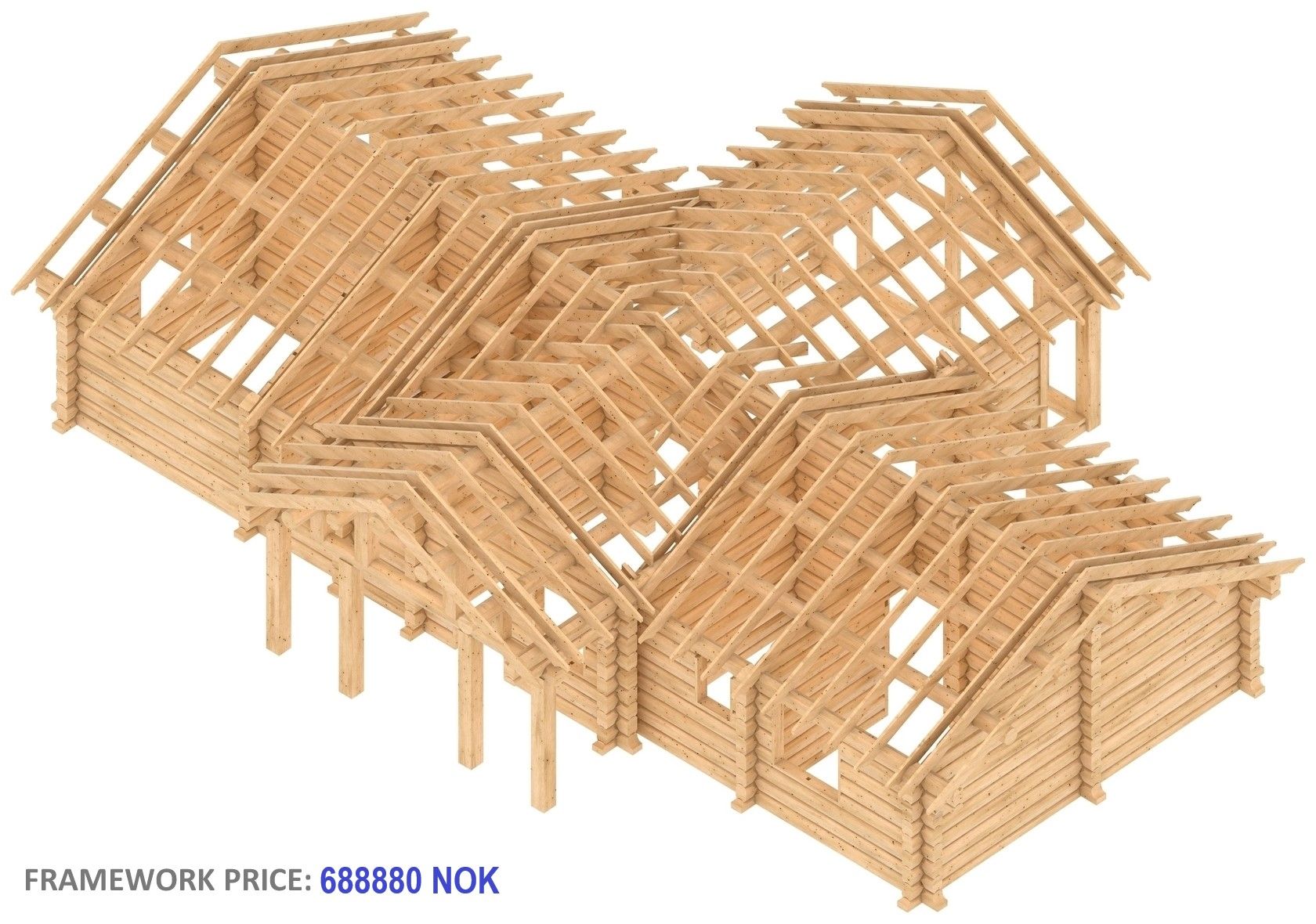

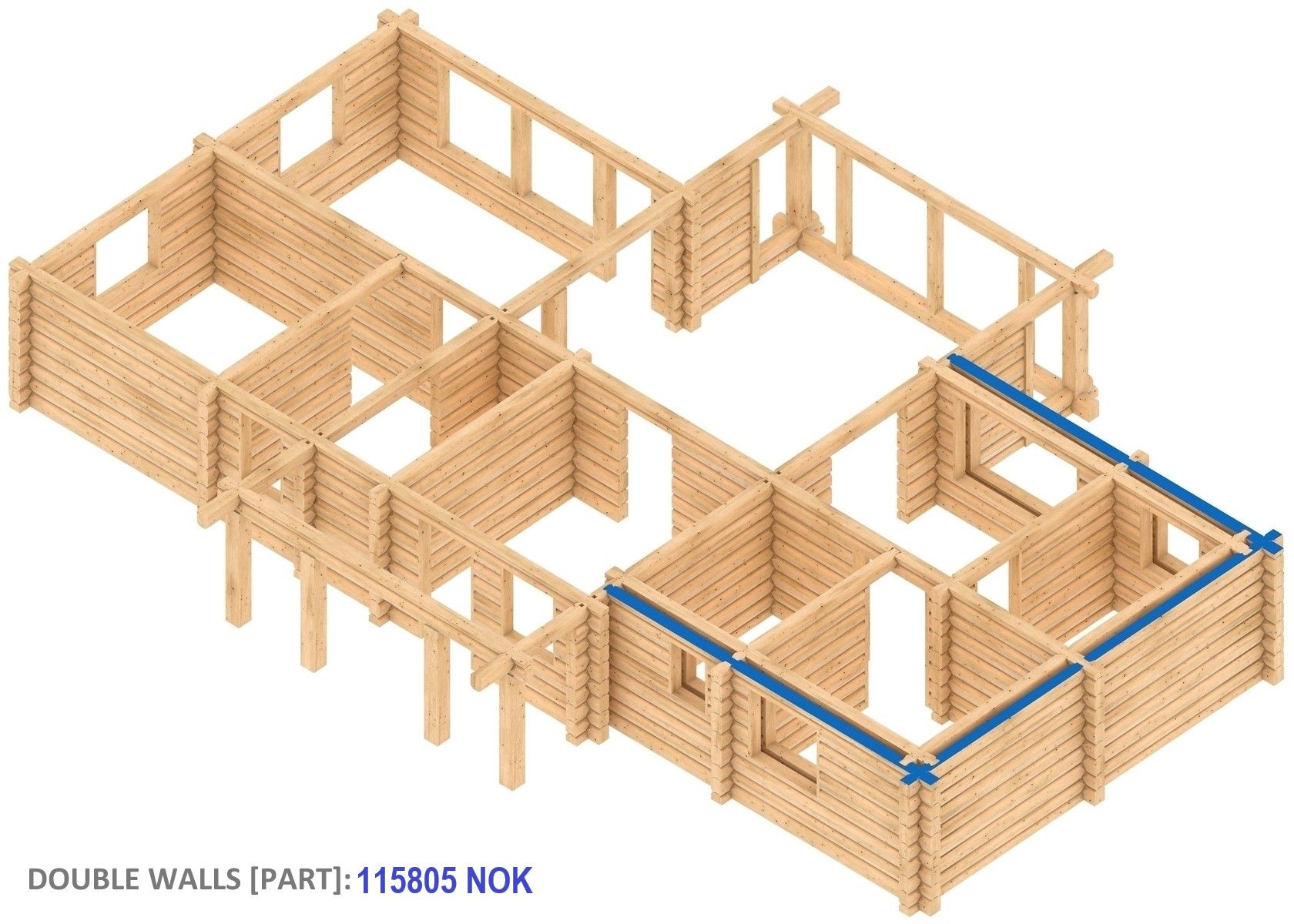
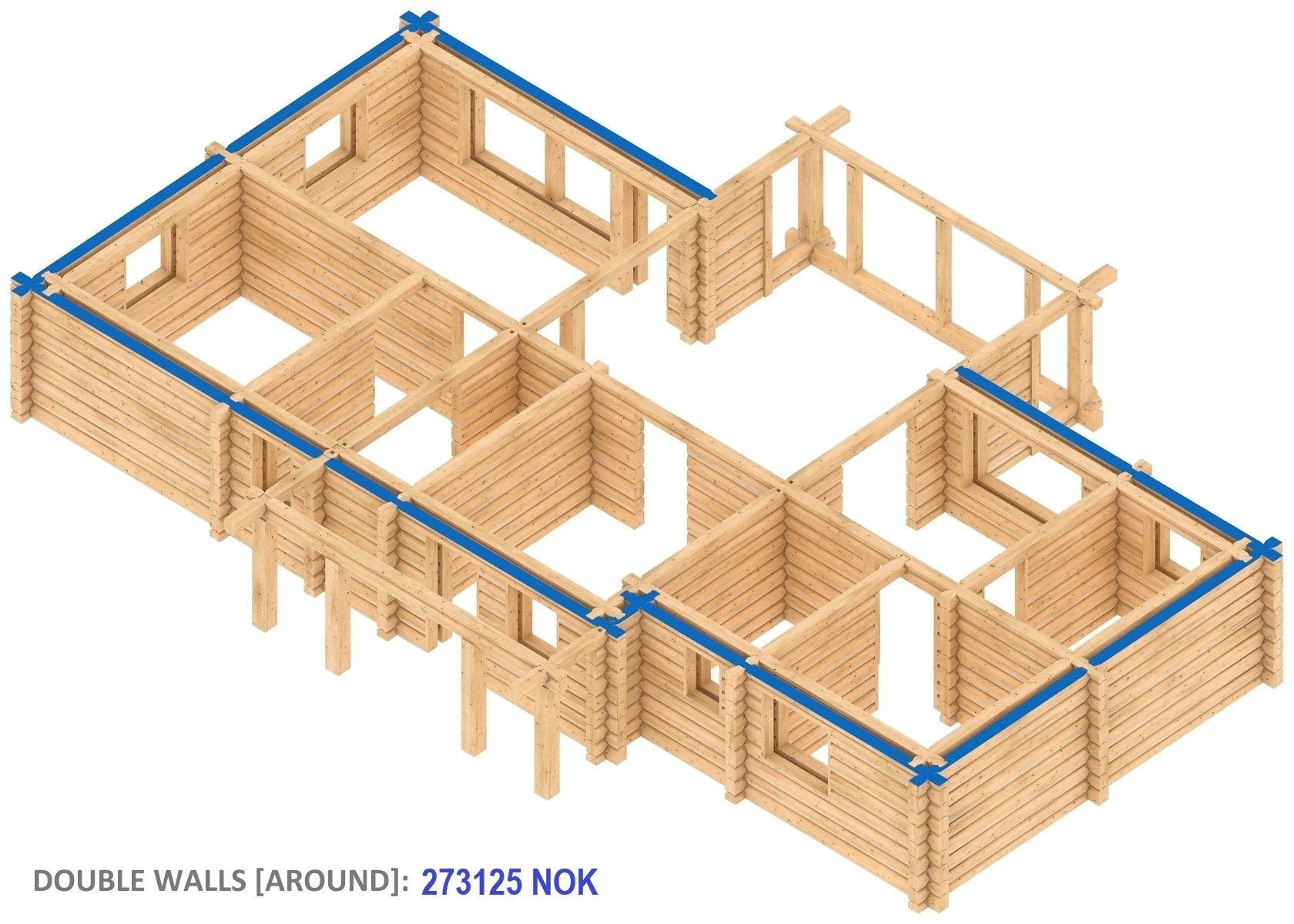
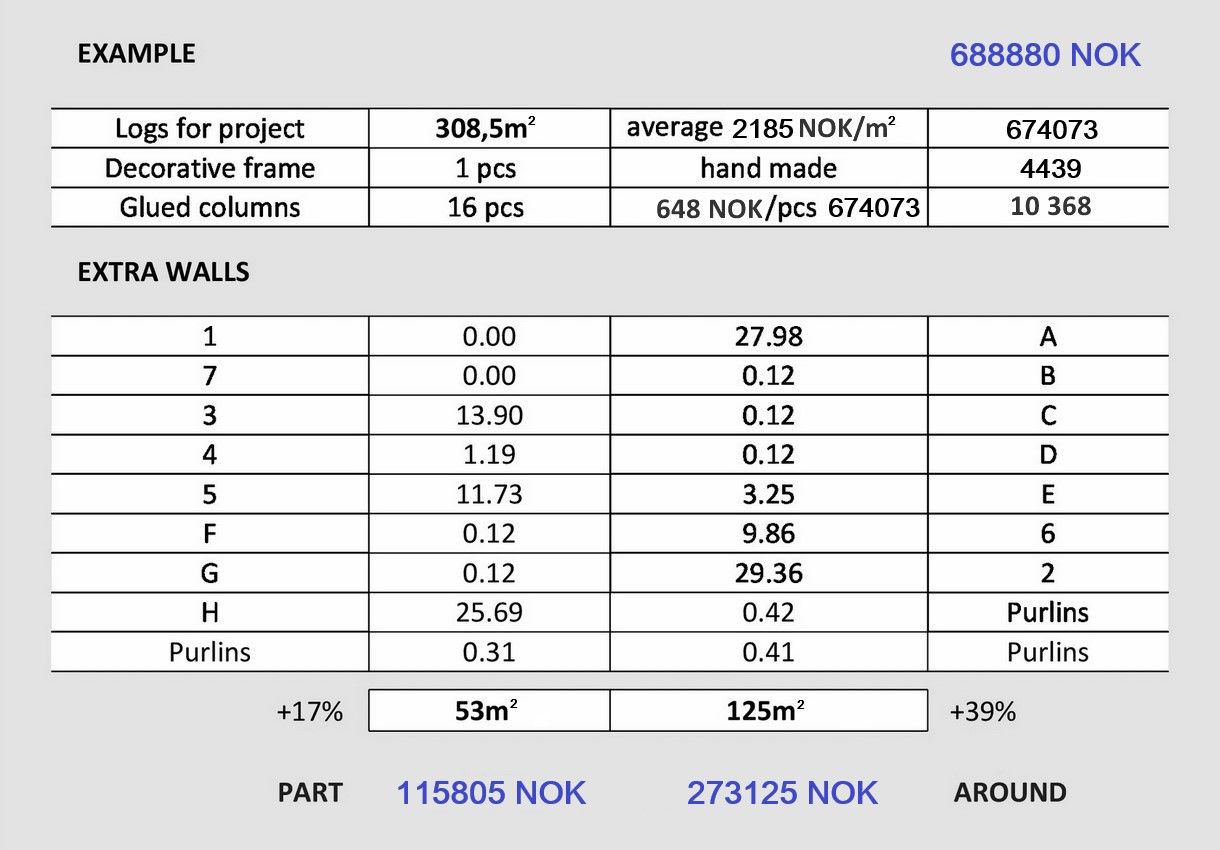
However, there will be several times lower percentage and a very small “share” mentioned above, if you attribute the cost of making the frame to the expected overall budget. The budget that includes both the purchase of the land plot and all construction and building erection costs. If you take the best offers from the advertisement portal www.finn.no, the share of making the log building frame is only 5–7% in the simple case, and only 1–3% more in the case of a double-walled frame. In addition, the savings in heating costs for double walls are guaranteed as a bonus. Try to calculate the share of the frame production (without delivery and assembly) just for your situation, and then judge for yourself. When evaluating shares and amounts for any estimate, calculation, offer or advertisement, be sure to find out the quality of the log building execution and be aware of the importance of this factor. Consider everything carefully and without haste. Especially from the point of view of the small proportion of the “share”. It is not worth unnecessarily endangering the fate of your investment. Financial issues require a serious approach.
Even without double walls, our log buildings have good thermal properties and tightness:
→ The U-value of the walls is 0.55 W/(m²K), which corresponds to the current heat standards, at least in Norway.
→ Log building frames convincingly withstand the pressure tests of buildings, even at one perimeter of external walls. In 2015, the construction company Østlaft Bygg AS performed the Blower Door test for a randomly selected log building, one year after the heating season, i.e. at the end of the log building’s drying and settling. The measurements were performed for a confidential customer and have shown compliance with both current and future expected Air Tight standards.
→ Log building frames pass convincing thermal tests and inspections. We offer a fragment from thermography, i.e. infra-red diagnostics for a log building in the Netherlands.
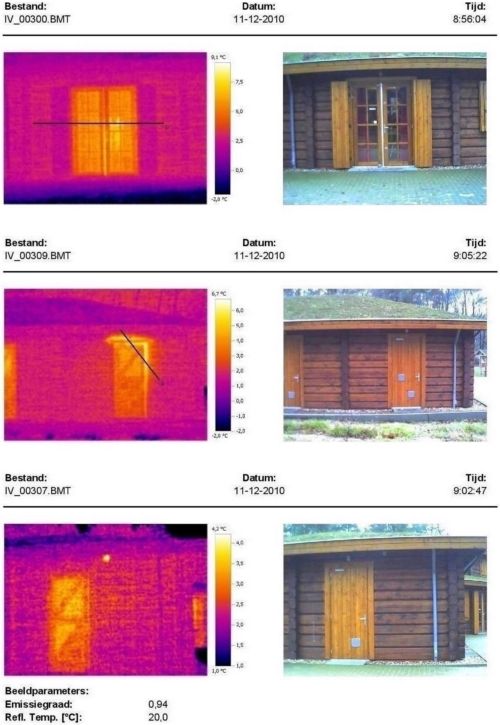
This protection is mainly provided by a “wind” pin. That is, a tongue, or cam and groove, built into the corner joint from inside. It is practically impossible to reproduce by hand. We offer you to get acquainted with other (practically unique) advantages of the product, in the section Quality.
The theme of double walls is relevant for people living in Sweden, Finland, Germany and other EU countries. In countries where Construction Boards require the isolation of a part of a log building, such as a living room. This is not very relevant for Norway yet, but this solution may be useful in the near future, when, as in many other parts of the world, the heat resistance standards of new buildings will be updated. Norway already tried to increase the heat norms for log buildings in 2015, but as a result of protests from log building industry companies, the planned norms were cancelled at that time and the topic was “frozen” indefinitely. A temporary compromise was reached, allowing the Norwegians to compensate with a thicker layer of thermal insulation on the roofs (in the direction of heat movement), as well as trying to put much better quality windows and entrance doors (in the main places of heat losses).
In turn, the Dutch are additionally investing in the development of complex engineering solutions, improving the electricity, heat and water supply in order to obtain certificates for energy-efficient, ecological, human and environmentally friendly buildings. We offer to look at the GreenCalc+ certificate for the same building in the Netherlands that is subject to thermography. The figure in the EIG index in short means that this log building is 4.19 times “better” than the buildings built in the 1990s.



